Description: This document outlines the parameters and functions of the "Advanced Routing and Forwarding" feature for LANCOM routers without WLAN.
Requirements:
Scenario: The aim is to restrict access between the networks Net 1, Net 2 and Net 3 on the LAN side of the router.
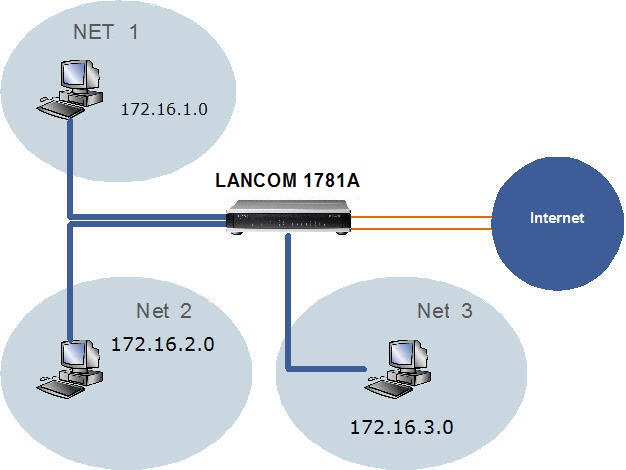 Net 1: Interface LAN1 (ETH -1), Network ID: 172.16.1.0 Net 2: Interface LAN2 (ETH -2), Network ID: 172.16.2.0 Net 3: Interfaces LAN3 (Eth-3) and LAN4 (Eth-3), Network ID: 172.16.3.0 Procedure: LANconfig is used to perform the configuration. A LANCOM 1781A is used for this example scenario.
Step 1: Allocating the interfaces to the networks. 1. Open your router's configuration with LANconfig. 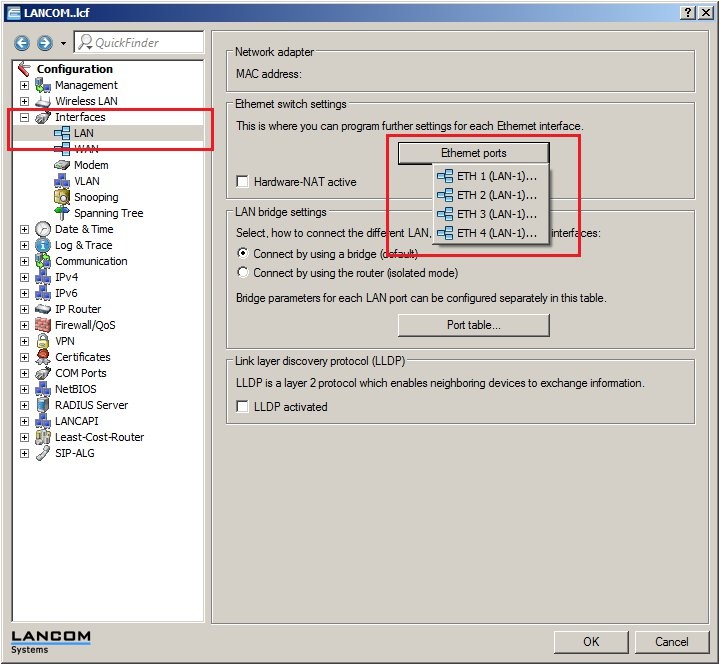 2. Allocate Ethernet interface 1 to the logical LAN-1. 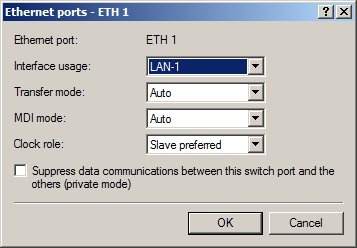 3. Allocate Ethernet interface 2 to the logical LAN-2. 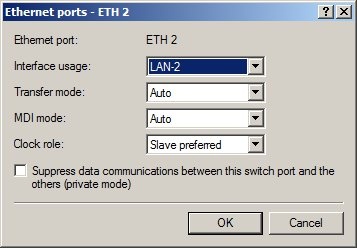 4. Allocate Ethernet interfaces 3 and 4 to the logical LAN-3. 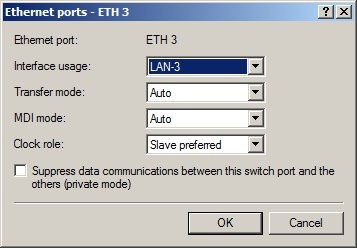 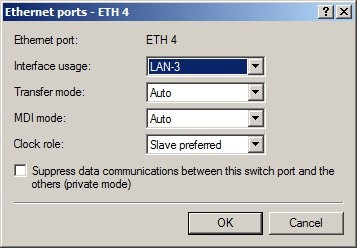 Step 2: Allocating physical interfaces and interface tags to the IP networks.
2. Allocate the interface and the interface tag to the IP networks.
 3. Net 1 operates on interface LAN-1 and uses interface tag 0, i.e. it can access all other networks. 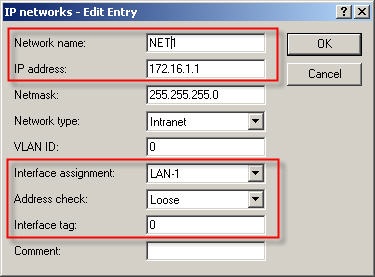 4. Net 2 operates on interface LAN-2 and is allocated interface tag 1, i.e. it cannot access any other local network. 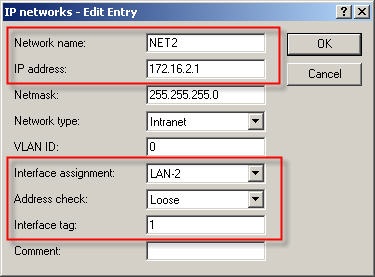 5. Net 3 operates on interface LAN-3 and is allocated interface tag 2, i.e. it cannot access any other local network. 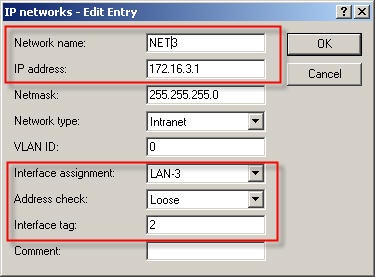 Step 3: Creating the routing entry. Clients from the networks can us all routes with routing tag 0. If the routing tag is no equal to 0 and not equal to the client’s own interface tag, the route from this network cannot be used. A default route with routing tag 0 can be used as a connection by all networks.  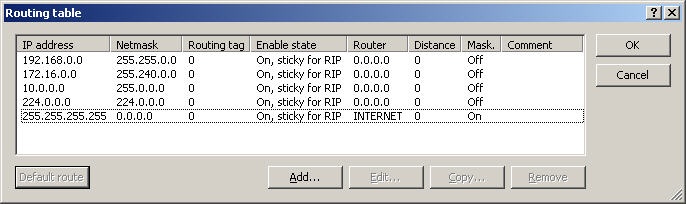 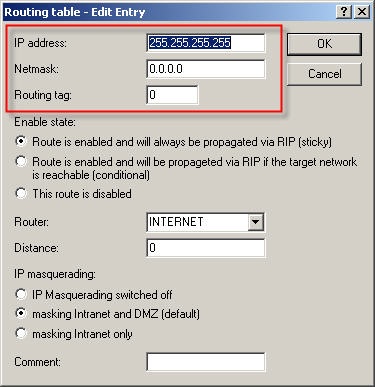
|