Description:
Remote access to our routers should preferably be implemented by means of a VPN client dial-in, for example using the LANCOM Advanced VPN Client. If this is not possible, it is often necessary to enable access via the WAN connection. This document explains the different ways of securing the remote access to a LANCOM router from the WAN.
Requirements:
Option 1: Enabling specific management protocols for WAN access
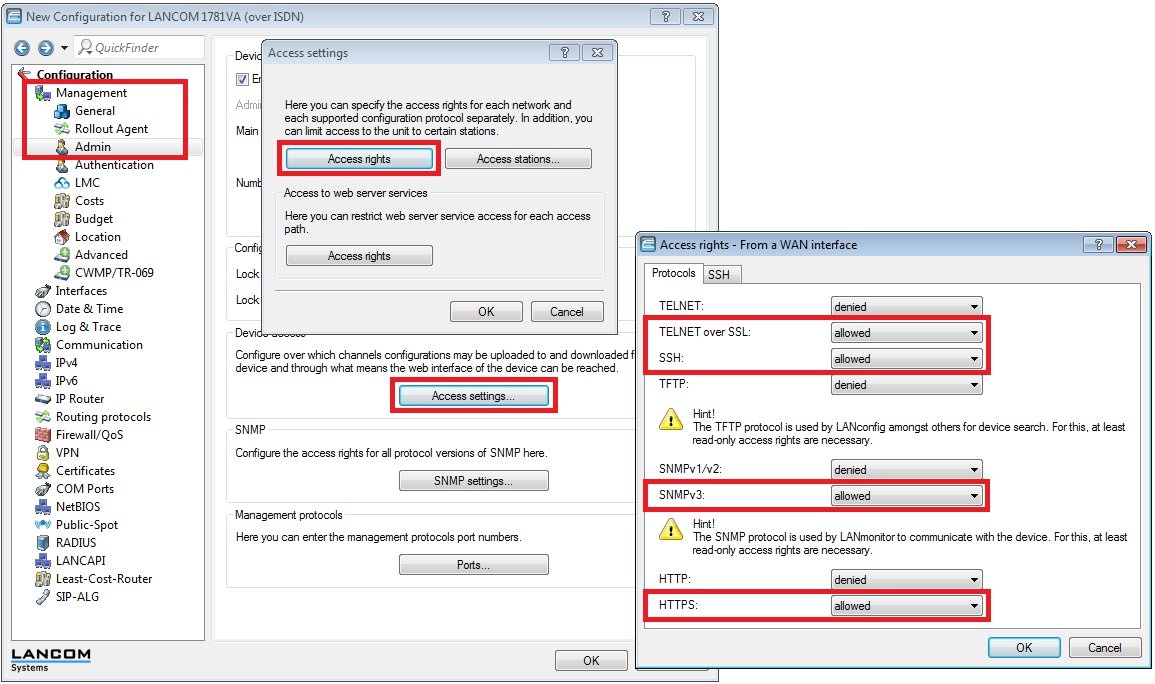
Enabling the access to management protocols from the WAN is done under Management -> Admin -> Access settings -> Access rights -> From a WAN interface.
- If access to a specific protocol from the WAN is to be enabled, then select allowed in the drop-down menu.
- If access from the WAN is not allowed, then select denied.
- If the router should only be accessible via VPN, then select only via VPN.
- By default, access to all of the management protocols from the WAN is denied.
Note:
Access to the router from the WAN should use encrypted protocols only (HTTPS, SSH, Telnet over SSL, SNMPv3).
Otherwise the password can be read as plain text!
Option 2: Enabling access to the router from specific IP addresses and/or IP networks only
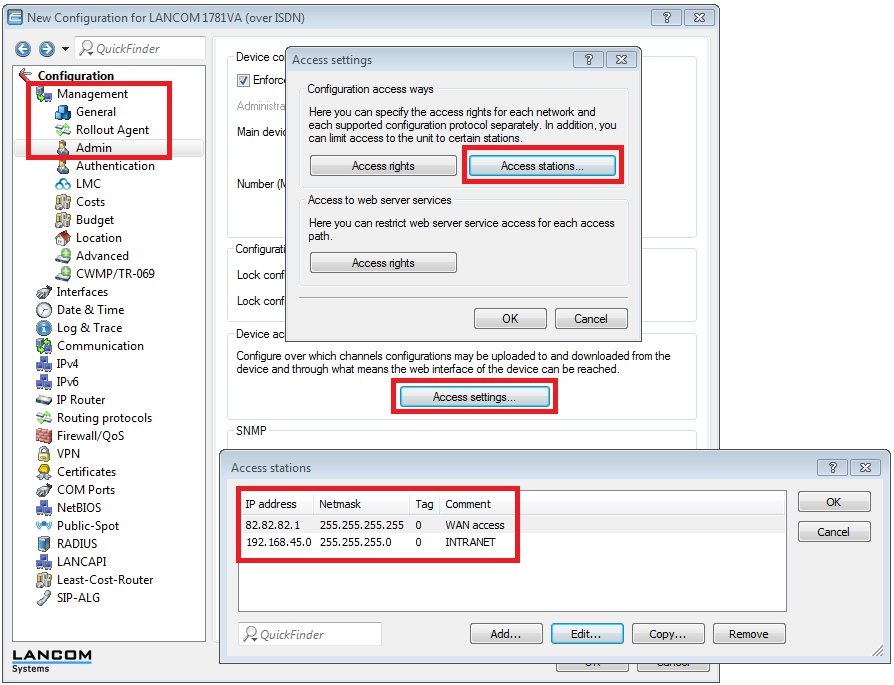
To allow access from the WAN from a specific public IP address only, go to Management -> Admin -> Access settings -> Access stations.
The access stations table is a whitelist. Access is only possible from the IP addresses or IP networks stored there.
Important:
The table
Access stations needs to contain all of the IP networks or IP addresses from which access to the router should be allowed. Consequently, the internal networks must also be stored here.
Otherwise access to the router will no longer be possible from the internal network!
Option 3: Configuration login lock
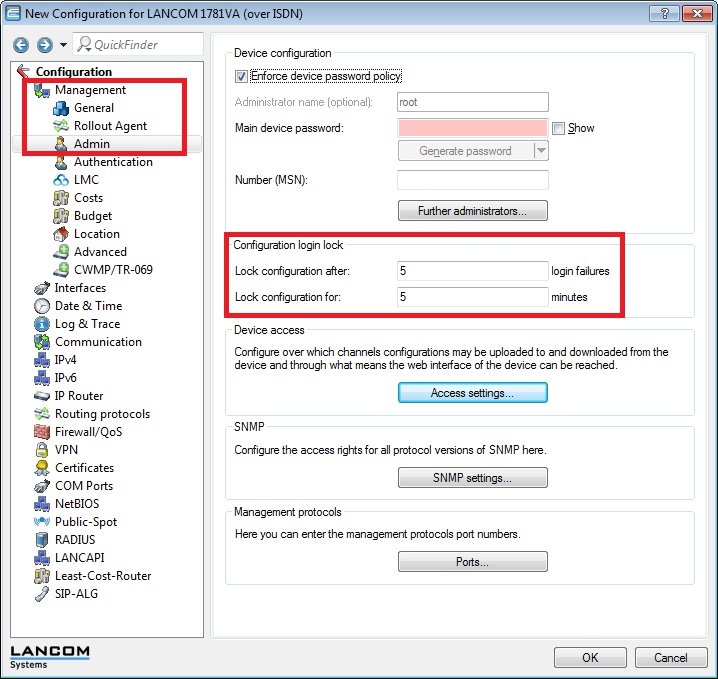
When management protocols are accessible from the WAN, you should expect frequent Internet-based brute force attacks attempting to gain access to the router. This is where brute-force protection comes into effect.
The relevant setting is to be found under Management -> Admin -> Configuration login lock. By default, 5 failed logins cause the management protocol to be locked globally for 5 minutes.
This management protocol is therefore not available for the duration of this lock, even from the internal network.
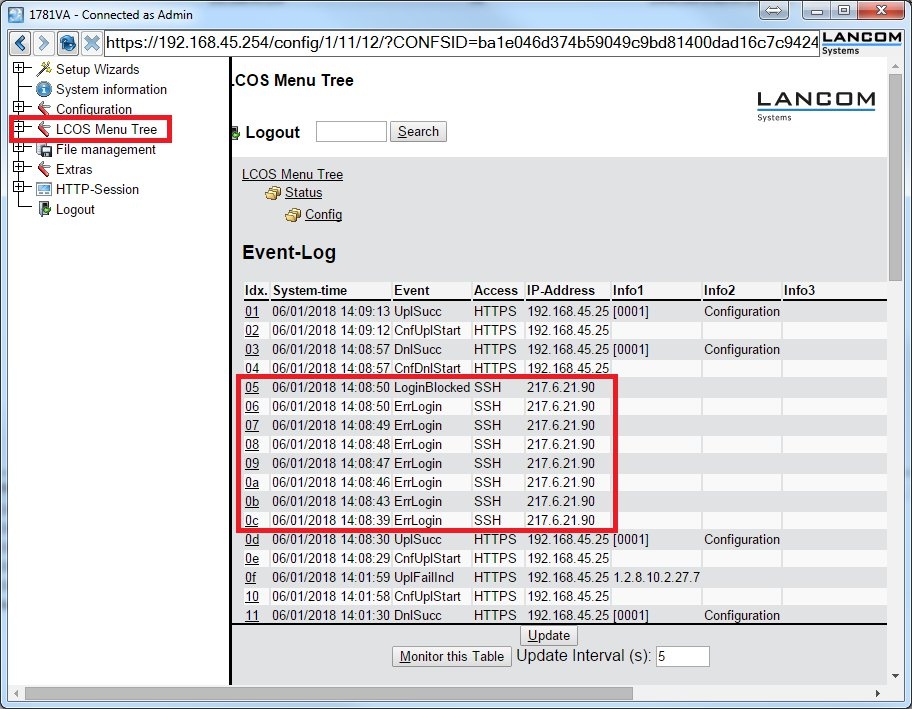
The
Event Log shows whether a management protocol was locked. In WEBconfig, it is located under
LCOS menu tree -> Status -> Config -> Event Log .
The following figure shows that too many failed login attempts were made via SSH. This protocol was locked as a consequence (LoginBlocked).
Option 4: Change the default port
Since brute-force attacks usually target the standard ports, we recommend that you change the ports used by any management protocols that are accessible from the WAN.
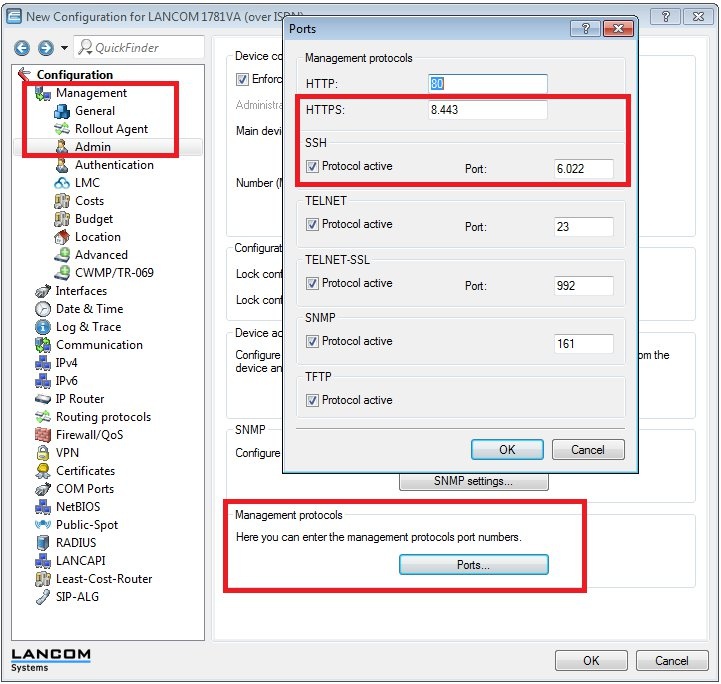
This setting is located under Management -> Admin -> Ports.
The port settings are global. Access to these management protocols from both the WAN and the LAN is only possible on the changed port.
|
|