| Seiteneigenschaften |
|---|
Question
What functions are provided by the Syslog selection tab for the router?
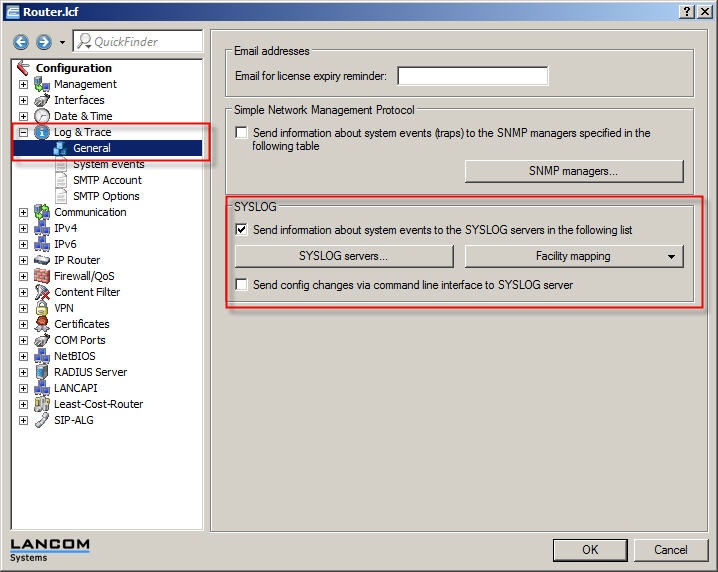
Answer:
in
Furthermore,
available
more
32 MB RAM => 2048 syslog messages more than 16 MB RAM => 1024 syslog messages more than 4 MB RAM => 256 syslog messages less than 4 MB RAM => 100 syslog messages
E.g. a LANCOM 1721 + VPN has 32 MB RAM avaliable and thus is able to store 2048 syslog
daemon
daemon
:
daemon under http://www.kiwisyslog.com/index.htm
|

Answer:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
