Description: In scenarios with a WLAN point-to-point connection between two sites, the failure of the P2P link could cause production downtime.
In this case it is worthwhile for the P2P link to have a backup over a VPN connection. This requires both locations to have an Internet connection.
This article describes how to set up a P2P link and create a VPN connection as a backup for the P2P link.
Requirements: - Both sites already have a configured and functional Internet connection
- Both sites have separate IP address ranges
Scenario: 1) The P2P link is implemented with separate access points - There are two sites: Each site has an access point and a router.
- The access points support the P2P link
- The routers use the P2P link between the access points to establish a plain Ethernet connection (IPoE).
- If the P2P link fails, a VPN connection is established between the two sites.
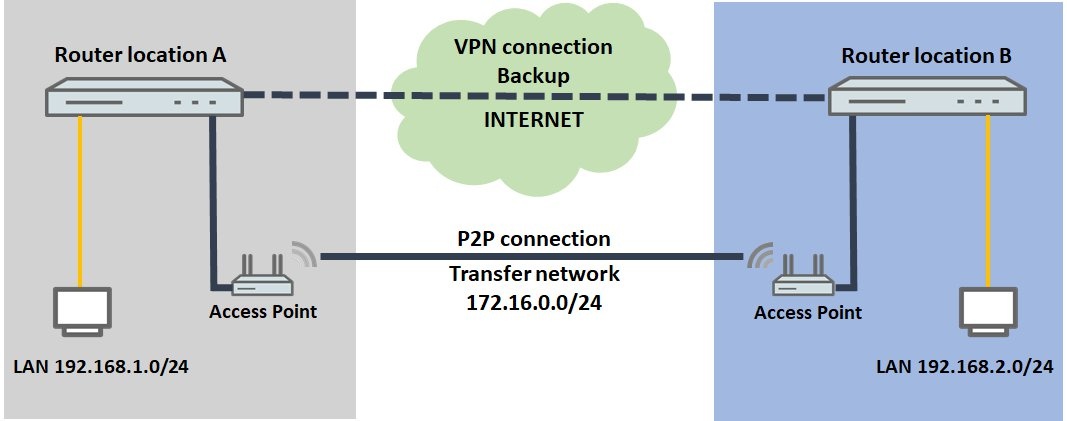 2) The P2P link is established using the WLAN module integrated in the router
2) The P2P link is established using the WLAN module integrated in the router - There are two sites: Each site has a WLAN router.
- The WLAN routers implement the P2P link
- The routers use the P2P link between them to establish a plain Ethernet connection (IPoE).
- If the P2P link fails, a VPN connection is established between the two sites.
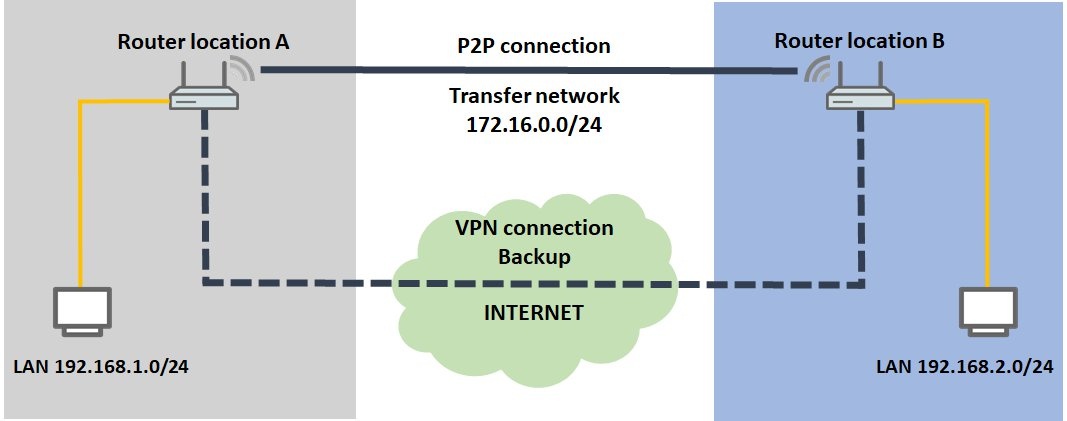 Procedure: Scenario 1: The P2P link is implemented with separate access points Configuration at site A: 1) Configuring router A:
Procedure: Scenario 1: The P2P link is implemented with separate access points Configuration at site A: 1) Configuring router A: 1.1) Set up a
VPN connection to router B using the Setup Wizard.
1.2) Set up a plain Ethernet connection (IPoE).
IP parameterstransfer networkcommunications between routers A and B- IP address: Give router A an IP address from the transfer network.
- Netmask: Enter the netmask of the transfer network.
- Default gateway: Enter the IP address of router B in the transfer network (see step 3.2.1).
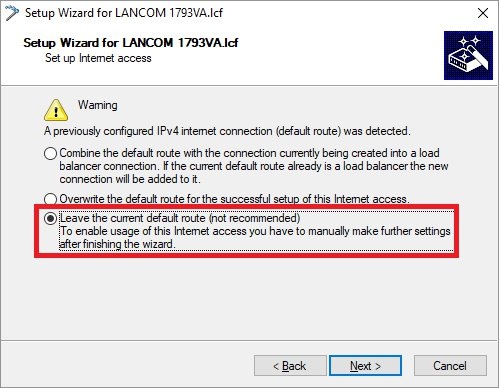
Important: The IP address range of the transfer network must not be in use at site A or site B, otherwise problems with routing will occur! 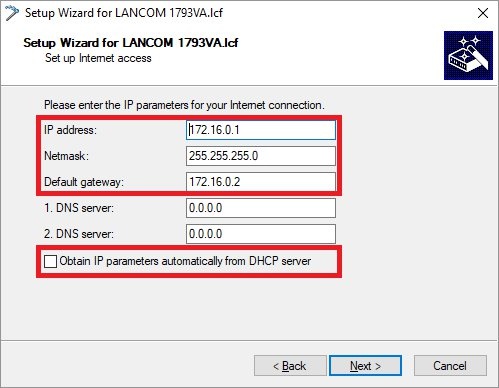 Leave the current default route
Leave the current default route- to use the current Internet connection.
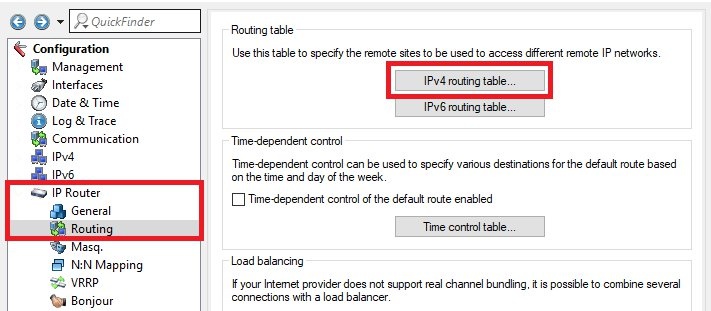
1.3) Open the configuration of the router in LANconfig and switch to the menu item
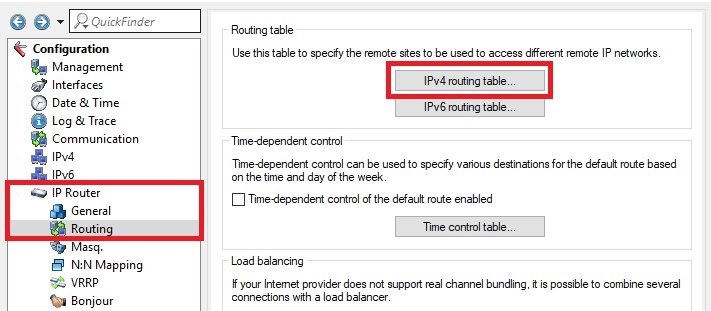
IP router -> Routing -> IPv4 routing table.
 routing entry of the VPN connection to site BRouterIPoE remote sitestep 1.2Important: IP masqueradingIP masquerading switched off
routing entry of the VPN connection to site BRouterIPoE remote sitestep 1.2Important: IP masqueradingIP masquerading switched off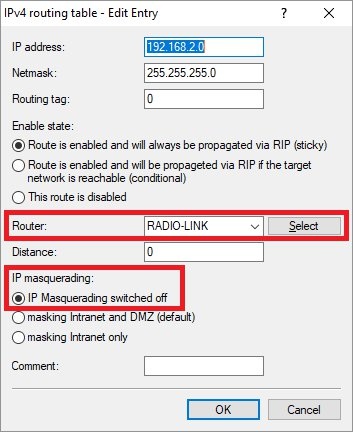
1.4) Navigate to the menu
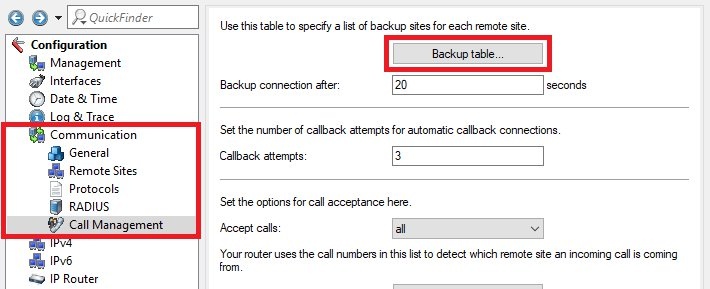
Communication -> Call Management -> Backup table.
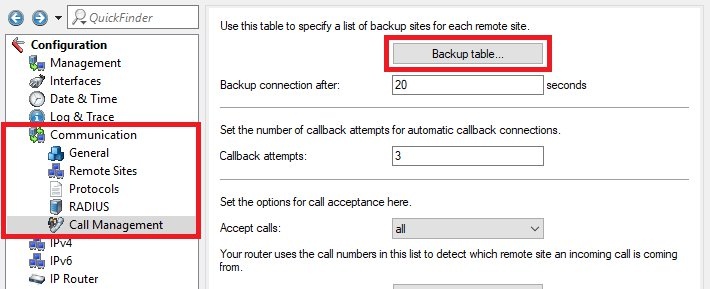
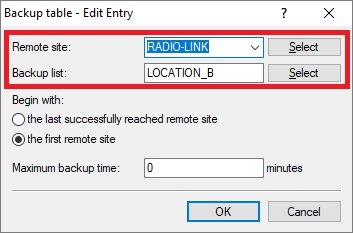
- 1.4.1) Store the following parameters:
- Remote site: From the drop-down menu, select the IPoE connection you created in step 1.2.
- Backup list: Select the VPN remote site (see Step 1.1).
1.5) Navigate to the menu
Communication -> Protocols -> Polling table.
Note: If you are using an IPoE or DHCPoE connection, ICMP polling must be set up for line monitoring. Otherwise, no backup connection will be established. 
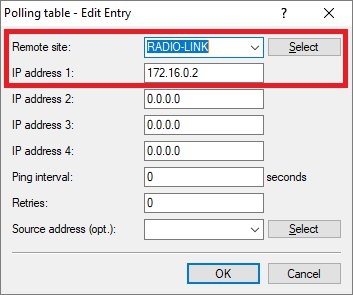
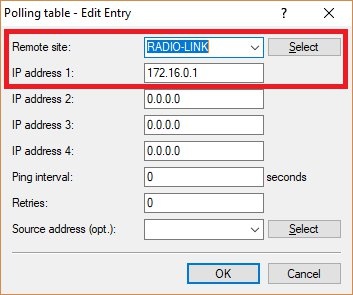
- 1.5.1) Create a new entry and enter the following parameters:
- Remote site: From the drop-down menu, select the IPoE connection created in step 1.2.
- IP address 1: Enter the IP address of router B in the transfer network (see step 3.2.1).
1.6) Write the configuration back to the router. This concludes the configuration of router A.
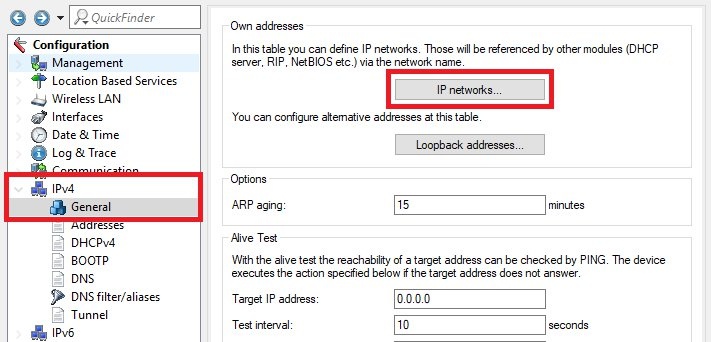
2) Configuring access point A: Important: The access point must be connected to the router’s DSL port. 2.1) Open the configuration for the access point in LANconfig and switch to the menu item
IPv4 -> General -> IP networks.
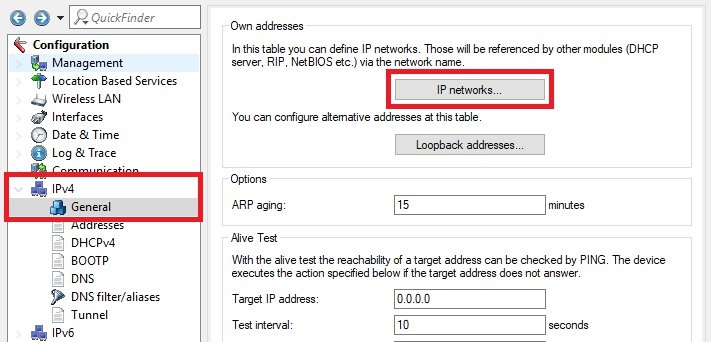 INTRANETIP address from the transfer network
INTRANETIP address from the transfer network- to access point A and enter the relevant
netmask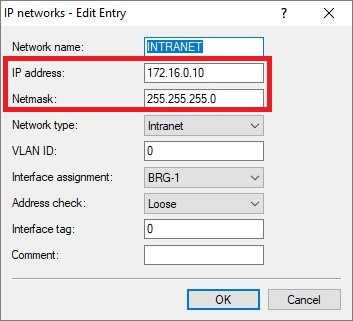
2.2) Write the configuration back to the access point.
2.3) Set up a
WLAN point-to-point link.
2.4) The configuration of access point A is complete.
Configuration at site B: 3) Configuring router B: 3.1) Set up a
VPN connection to router B using the Setup Wizard.
3.2) Set up a plain Ethernet connection (IPoE).
IP parameterstransfer networkcommunications between routers A and B- IP address: Give router B an IP address from the transfer network.
- Netmask: Enter the netmask of the transfer network.
- Default gateway: Enter the IP address of router A in the transfer network (see step 1.2.1).
Important: The IP address range of the transfer network must not be in use at site A or site B, otherwise problems with routing will occur! 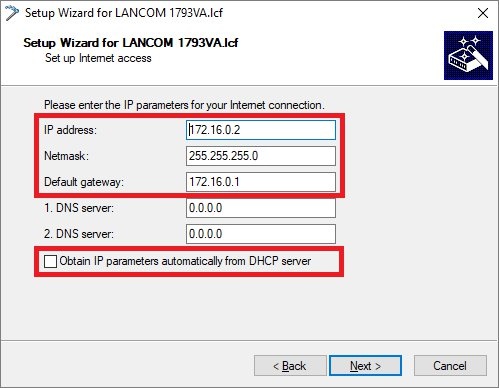 Leave the current default route
Leave the current default route- to use the current Internet connection.
3.3) Open the configuration of the router in LANconfig and switch to the menu item
IP router -> Routing -> IPv4 routing table.
 routing entry of the VPN connection to site ARouterIPoE remote sitestep 3.2Important: IP masqueradingIP masquerading switched off
routing entry of the VPN connection to site ARouterIPoE remote sitestep 3.2Important: IP masqueradingIP masquerading switched off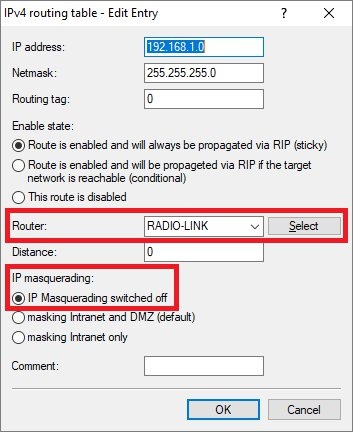
3.4) Navigate to the menu
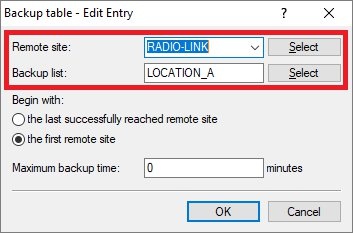
Communication -> Call Management -> Backup table.
- 3.4.1) Store the following parameters:
- Remote site: From the drop-down menu, select the IPoE connection you created in step 3.2.
- Backup list: Select the VPN remote site (see step 3.1).
3.5) Navigate to the menu
Communication -> Protocols -> Polling table.
Note: If you are using an IPoE or DHCPoE connection, line monitoring by means of ICMP polling must be set up. Otherwise, no backup connection will be established. 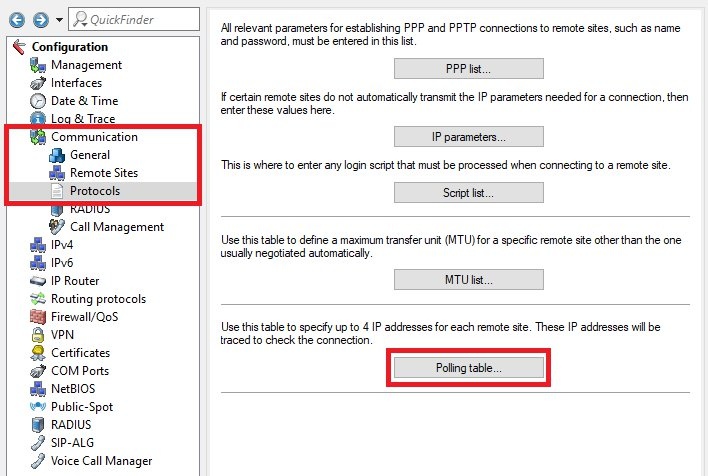
- 3.5.1) Create a new entry and enter the following parameters:
- Remote site: From the drop-down menu, select the IPoE connection created in step 3.2.
- IP address 1: Enter the IP address of router A in the transfer network (see step 1.2.1).
3.6) Write the configuration back to the router. This concludes the configuration of router B.
4) Configuring access point B: Important: The access point must be connected to the router’s DSL port. 4.1) Open the configuration for the access point in LANconfig and switch to the menu item
IPv4 -> General -> IP networks.
 INTRANETIP address from the transfer networkaccess point Bnetmask
INTRANETIP address from the transfer networkaccess point Bnetmask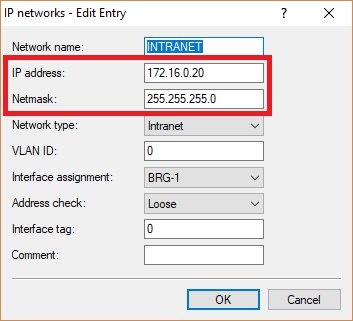
4.2) Write the configuration back to the access point.
4.3) Set up a
WLAN point-to-point link.
4.4) The configuration of
access point B is complete.
Scenario 2: The P2P link is established using the WLAN module integrated in the router
The configuration of the two routers corresponds to that of scenario 1. Some additional adjustments still have to be made.
The following steps must be performed on both routers.
1) Set up a WLAN point-to-point link.
2) Switch to the menu Interfaces -> WAN -> Interface settings -> DSLoL.
LAN interface- , use the drop-down menu to select the
P2P interface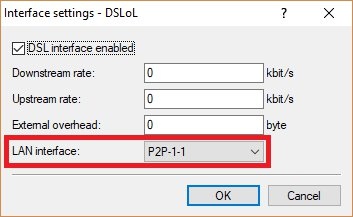
3) Switch to the menu
Communication -> Remote sites -> Remote sites (DSL).
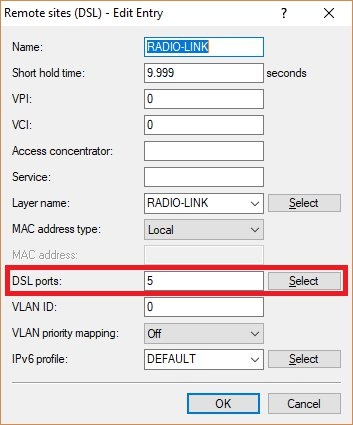
 IPoE remote sitesteps 1.2 and 3.2DSL portDSLoL
IPoE remote sitesteps 1.2 and 3.2DSL portDSLoL- Router with four LAN ports: DSL port 5
- Router with two LAN ports: DSL port 2